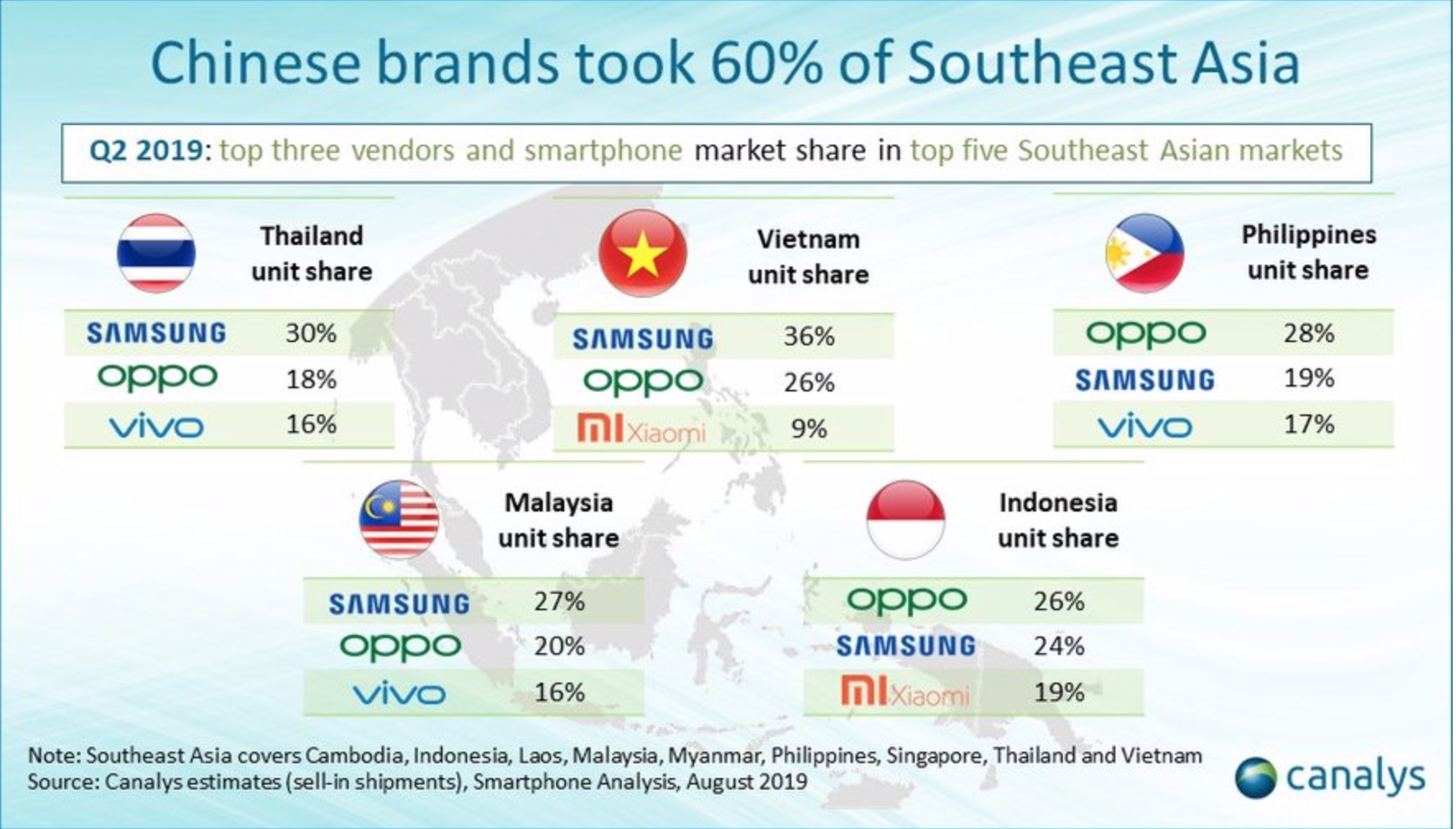
The Southeast Asian smartphone market grew modestly in Q2 2019, by 2% year on year, with 30.7 million units shipped during the quarter, reversing several quarters of decline. Southeast Asia did better than other parts of Asia, and Greater China, which recorded a year-on-year decline. Samsung shipped 7.7 million units, returning to growth of 5%, after three quarters of decline. Close behind was Oppo, which shipped 7.3 million units, recording its best-ever quarter’s performance with 49% year-on-year growth. Vivo remained third, shipping 4.1 million smartphones, while Xiaomi displaced Huawei to take fourth place, shipping 3.7 million units. Realme entered the top five for the first time, shipping 1.6 million smartphones, having only been in Southeast Asia for three quarters.
Chinese brands, mostly Oppo, Vivo, Xiaomi, Realme and Huawei, shipped a total of 19.0 million units in Q2, to take a 62% share in the region, a big jump from 50% in the same quarter last year. “Southeast Asia is popular for new brands, as the chances of success are higher than in other parts of the world,” said Canalys Analyst Matthew Xie. “With 75% of shipments consisting of sub-US$200 models, the market here is focused on mid-to-low-end smartphones, a segment where brand loyalty is low. Given the vast population, development of online and logistical infrastructure, and increasing local production capability, vendors are investing heavily to secure business resources and consumer awareness.”
Given the myriad brand choices and ample supply of devices, most markets in Southeast Asia recorded sequential increases in Q2. This was also helped by aggressive promotions from the top vendors to take advantage of a weakened Huawei. While people are likely to buy even more phones during the rest of the year, thanks to a range of festive promotions, vendors will face an uncertain time as Samsung threatens to erode their market shares with its new devices.