Shortcut files are fast becoming a common vehicle used in targeted attacks to deliver malware into organizations. Symantec has observed a variety of ways that shortcut files are being used to penetrate networks because they allow for evasion in threat detection by security products.
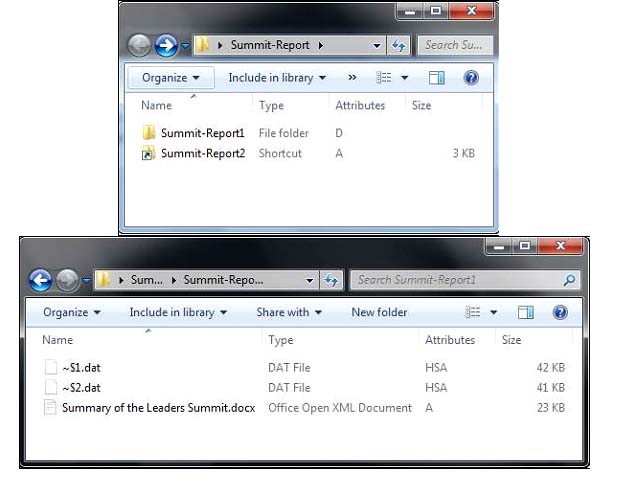
In this latest example, an email is circulated with an attachment and a shortcut file which is used to reassemble the malware. The email used for this attack included an archive file as an attachment, which contains a shortcut file with an icon of a folder, along with a real folder containing a Microsoft document file and two hidden files with .dat file extensions.
Keen users will have noticed that only one of the two Summit-Report folders is an actual folder, with the other being a shortcut file. A look inside the Summit-Report 1 folder reveals the components of the malware file. However, clicking on the shortcut will execute the assembling of the malware.
 Shortcut files are typically simple and cost efficient to use by cybercriminals. They do not require the use of exploits, which can be more resource intensive and also requires the victim’s computer to be vulnerable. Icons can easily be made to look like folder or document files. Once an attacker prepares the malicious files, they then only have to write one line of script and the attack is ready.
Shortcut files are typically simple and cost efficient to use by cybercriminals. They do not require the use of exploits, which can be more resource intensive and also requires the victim’s computer to be vulnerable. Icons can easily be made to look like folder or document files. Once an attacker prepares the malicious files, they then only have to write one line of script and the attack is ready.
Symantec recommends that network administrators filter out the shortcut filetype at the gateway of the network as there are no practical reasons for emails to contain shortcut files in normal circumstances. Recipients should also remain vigilant and look out for emails with suspicious files and only open these files when they receive it from someone trustworthy.
For more information, please proceed to the Symantec Security Response blog post or follow us on Twitter at @SymantecASEAN.