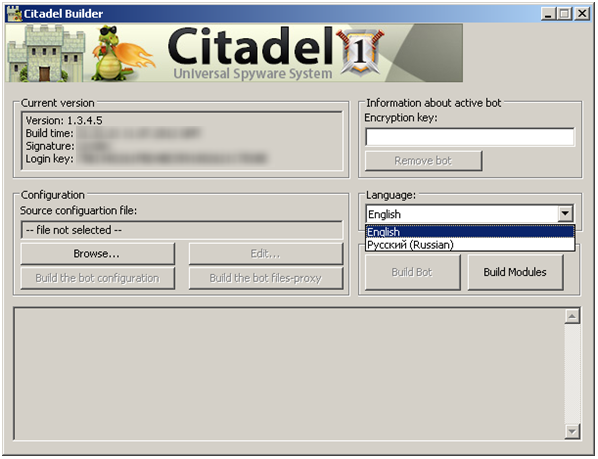
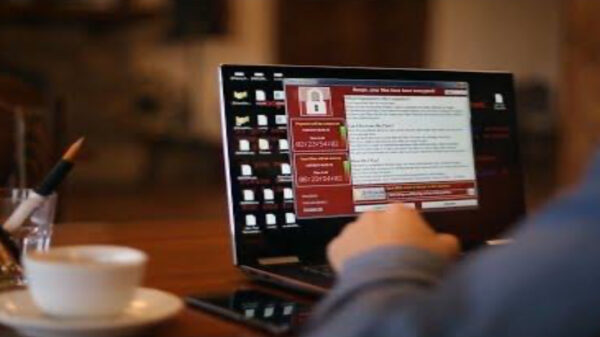
Citadel, a banking Trojan which has been in existence since 2011, has been recently taken down by Microsoft and members of the financial services industry and the FBI. The takedown operation resulted in over 1,000 Citadel botnets being taken offline.
As with most banking Trojans, Citadel is a full crimeware kit, providing the attackers with payload builders, a command and control (C&C) server infrastructure, and configuration scripts to target various banks. Citadel is a descendant of that other behemoth of the financial Trojan world, Trojan.Zbot (Zeus). It came into existence after the Zeus source code was leaked in 2011, with criminal groups taking that code and enhancing it.
Citadel is aimed at a more “exclusive” attacker market than its more widespread predecessor, Zeus. The Citadel kit is sold through underground Russian forums and typically costs around $3,000, compared to $100 for the SpyEye and leaked Zeus kits. Citadel users have to also fork out a further $30-$100 to purchase Web inject code for the banks that they wish to target. Additionally, even if attackers have that money to spend, there is a strict vetting process with referrals required for new purchasers.
Citadel infections have spread around the globe so security experts such as Symantec welcome news of the takedown of these Citadel botnets.
“While these takedowns may not eliminate the threat of Citadel completely, it certainly disrupts current campaigns and sends out a clear message to attackers that their actions are being monitored,” says Symantec in its company blog. “Symantec also welcomes the cooperation between the public and private sector in taking action against this threat.”